DORSODYNIAS
Dorsodynia or pains in loin are among the most frequent complaints of patients in all-medical practice. They take the second place (after respiratory diseases) on the frequency of requests for a medical care.
Causes of back pain
There is a set of the states of health of a person which lead to emergence of pain in a spine (a back and a loin). Some of them are congenital as Bifid's (spina Bifida) back, others are formed with age (osteochondrosis, a spondylosis, a spondylarthrosis, an osteoporosis etc). However, the majority of the reasons of pain in a spine (a back and a loin) are connected with the same exercise stresses at work (sitting driving in a car or sedentary work at the computer) and spine injuries.
People with active sport lifestyle suffer from pains in spine (back and loin) much less often. Prophylaxis of development of osteochondrosis of a backbone and emergence of pain in a spine (a back and a loin) is first of all gymnastic activity, sport, and active recreation. It takes out day load of the same muscles, ligaments and joints of lumbar part of a spine.
Back pain is a peculiar payment of mankind for bipedalism when the greatest load is on a lumbar part of a spine carrying the main mass of a human body. Harmful impact on a spine is exerted also by a hypodynamia, improper feeding, obesity, stresses.
The dorsodynia can be parted on primary and secondary.
The reasons of primary pain (pathology of a spine column) are dystrophic and functional changes in joints of vertebrae, intervertebral disks, muscles, tendons, ligaments.
Secondary pains are connected with traumatic damages of a spine, tumoral and infectious processes, diseases of internals, including organs of a small pelvis at women, osteoporosis and other pathology. It is a peculiar alarm signal about malfunctions in an organism. There are a lot of different reasons of pain in spine which aren't surely connected with spine pathology. Especially common causes of a constant back pain are benign and malignant diseases of pelvic organs at women and men (endometriosis, hysteromyoma, dysmenorrhea, inflammatory diseases of ovaries, lesions of large vessels, kidneys, chronic prostatitis, some illnesses of nervous system).
The general causes of pain in a spine (back and loin) include:
- muscle spasm (acute or chronic);
- protrusion or hernia of an intervertebral disk (with possible pinching of a nerve);
- degenerative processes of spine (osteochondrosis, spondylosis, spondylolisthesis);
- Sheermana-Mau's illness;
- Bekhterev's illness;
- stenosis of the vertebral channel;
- sacroileitis (inflammation of a sacroiliac joint);
- arthrosis of a sacroiliac joint;
- arthrosis of an intervertebral joint (spondylarthrosis) etc.
Back pain can occur if you:
- spend much time driving a car or using a computer;
- do dynamic manual work with change of position of a body (especially if your specialty is bound to a serious exercise stress).
- Excessively load yourself in a gym or fitness club. Be extremely careful if you have recently begun to train!
- have mainly sedentary (office workers) or standing (the sellers, waiters serving street advertizing, surgeons) way of life.
- suffer from overweight.
Additional risk for women:
- You are pregnant or recently travailled.
- You reached the postmenopause disposing to development of osteoporosis.
The most frequent cause of a back pain is osteochondrosis of spine which is shown as a result of jamming of the nervous roots departing from a spinal cord at this or that level.
Back pain at lumbar osteochondrosis
Back pains at osteochondrosis can amplify at cough and sneezing, at any movements, especially at trunk inclinations forward. Along with a back pain, lumbar osteochondrosis can be shown by disturbance of sensitivity of certain areas of skin or muscles of the lower half of a trunk and legs, weakening or disappearance of tendinous reflexes of legs. As a rule, at osteochondrosis the curvature of lumbar part of a spine is observed. Depending on a part in which there is a curvature distinguish scolioses (a curvature to the right or to the left), lordoses (convexity forward) and kyphosis (delection of lumbar part or even its convexity back).
If at osteochondrosis there is pinching of spinal cord, disturbance of emiction or defecation and also disturbance of sensitivity of bladder or genitals are observed.
The most often lumbar osteochondrosis is shown by radicular pains - i.e. developing as a result of jamming of the nervous roots departing from spinal cord at this or that level.
Low back pain LBP
(LBP) is a common disorder involving the muscles, nerves, and bones of the back. Pain can vary from a dull constant ache to a sudden sharp feeling. n the common presentation of acute low back pain, pain develops after movements that involve lifting, twisting, or forward-bending. The symptoms may start soon after the movements or upon waking up the following morning. The description of the symptoms may range from tenderness at a particular point to diffuse pain. It may or may not worsen with certain movements, such as raising a leg, or positions, such as sitting or standing. Pain radiating down the legs may be present. The first experience of acute low back pain is typically between the ages of 20 and 40. Low back pain is not a specific disease but rather a complaint that may be caused by a large number of underlying problems of varying levels of seriousness. The majority of LBP does not have a clear cause but is believed to be the result of non-serious muscle or skeletal issues such as sprains or strains. Obesity, smoking, weight gain during pregnancy, stress, poor physical condition, poor posture and poor sleeping position may also contribute to low back pain. A full list of possible causes includes many less common conditions.Physical causes may include osteoarthritis, degeneration of the discsbetween the vertebrae or a spinal disc herniation, broken vertebra(e) (such as from osteoporosis) or, rarely, an infection or tumor of the
Waist pains at sciatica
 Sciatica (Greek ischiás, from ischíon — a pelvis, a hip), lumbar and sacral radiculitis, disease of back of lumbar and sacral part of spinal cord and, mainly, sciatic nerve.
Sciatica (Greek ischiás, from ischíon — a pelvis, a hip), lumbar and sacral radiculitis, disease of back of lumbar and sacral part of spinal cord and, mainly, sciatic nerve.
This nerve is the largest in a human body. It originates at five various levels of spinal cord in lumbar part of spine. Then the sciatic nerve goes down a leg, being divided into smaller nerves which go to a hip, a knee, a shin, an ankle joint, a foot and fingers. Because of the big extent of a sciatic nerve and its close connection with many bodies, diseases of a sciatic nerve can be met very often.
Pain at sciatica is different - lightning pain, burning, pricking, "goosebumps" and numbness at the same time. Pain at a sciatica can be such cruel that the patient can't sleep or perform such necessary operations as to sit, stand, go, bend or turn.
Lightning pain occurs in a clunis and on the back surface of a leg, as a rule on one side of a body. As well as at lumbago, pain amplifies at change of position of a body. Painful nodules in muscles of a hip and a shin can be found.
Attacks of lumbago and sciatica can occur more than once during life. Therefore it is very important to reveal type of loading or position of a body which provoke their emergence. It will allow preventing development of attacks. Attacks of diseases are stopped by analgetics, anesthetizing blockade to the area of spine, and also special actions on stretching of spine and clunis area. Treatment of a syndrome has to be complex.
Pain in lumbar area is one of characteristic symptoms of a disease of kidneys.
The constant "blunt" aching pain in a costovertebral angle from a sore kidney is characteristic of pathology of kidneys. Often pain irradiates to hypochondrium, area of a belly-button and a lower part of stomach. The described pain is caused by fast stretching of the renal capsule, for example, at an edema because of acute pyelonephritis or blocked ureter. Meanwhile many diseases - chronic pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis, malignant tumors and polycystosis of kidneys - proceed without pain as are followed by very slow stretching of the renal capsule.
Considering that the same symptom can be a consequence of various diseases, any treatment should be begun with a visit to the doctor and determinaation of the exact diagnosis.
Treatment of back pain
Lyapko applicators can be used for putting off of acute pain and for prophylaxis of dorsodynias and loin. They influence dermal receptors, points and reflex zones, cause proper responses of an organism. Lyapko applicators help to awake immune system, give it additional strength for successful fight against illness. Adjoining to a skin, needles of an applicator stimulate emission of internal drugs of a person, putting "the internal doctor" of the person into operation.
At neurologic symptoms of osteochondrosis of spine place applicators Quadro along all spine. You can also influence with applicators on all area of neck, back, loin and pelvis. Chronic radiculites with prolonged exacerbation and abaissement of functions assume prolonged treatment within several months (3 courses), with breaks for 1-2 weeks.
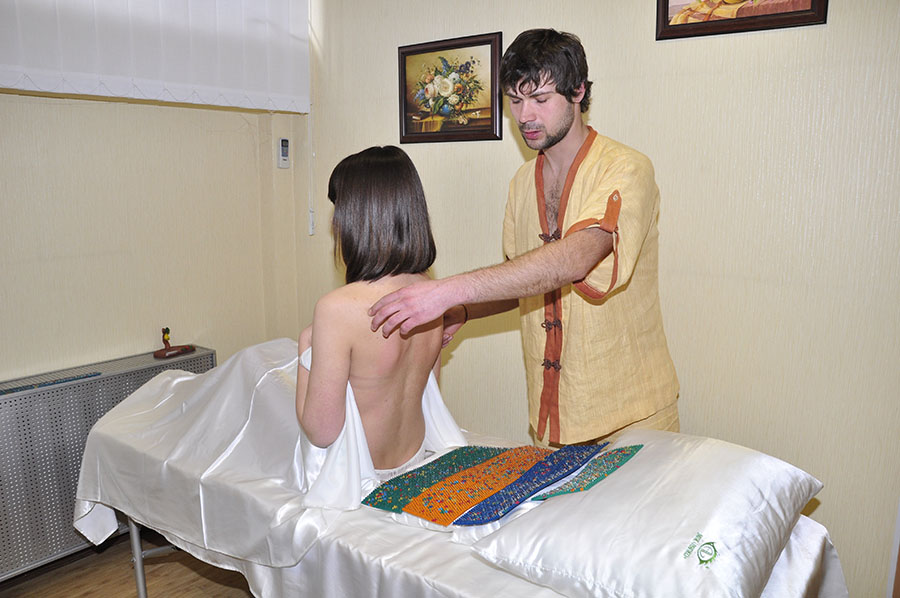

Applicator for the back - how to choose
Areas of numbness and pain and also zones adjoining to them zones can be additionally processed with roller-applicators. It is also necessary to wear durably small applicators in points of the maximum pain (lumbar area on the way of sciatic nerve).

At neurologic symptoms of osteochondrosis of spine complex treatment is the most effective. Applications on specified zones and points are recommended to be combined with use of creams, with usual massage or massage by means of Pharaoh massager. In the absence of contraindications, it is expedient to combine applications with sessions of manual therapy.
It is better to finish a session with application of feet (5-10 minutes), using applicators Insoles Plus.
In case of chronic osteochondrosis of thoracolumbar, lumbosacral part of spine or for prophylaxis, wearing of small applicators and belt-applicators in areas of pain (loin, sciatic nerve) is recommended.
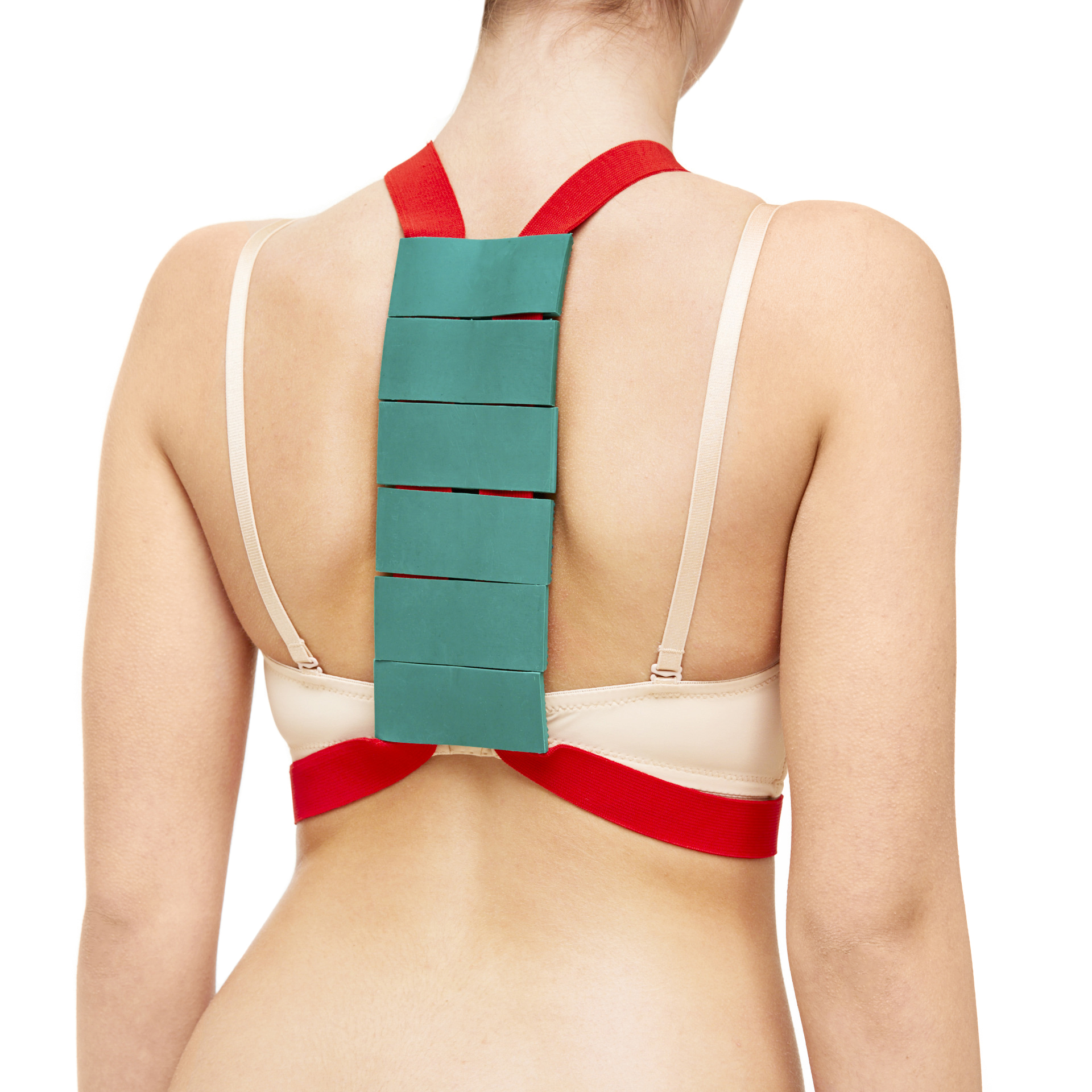 |
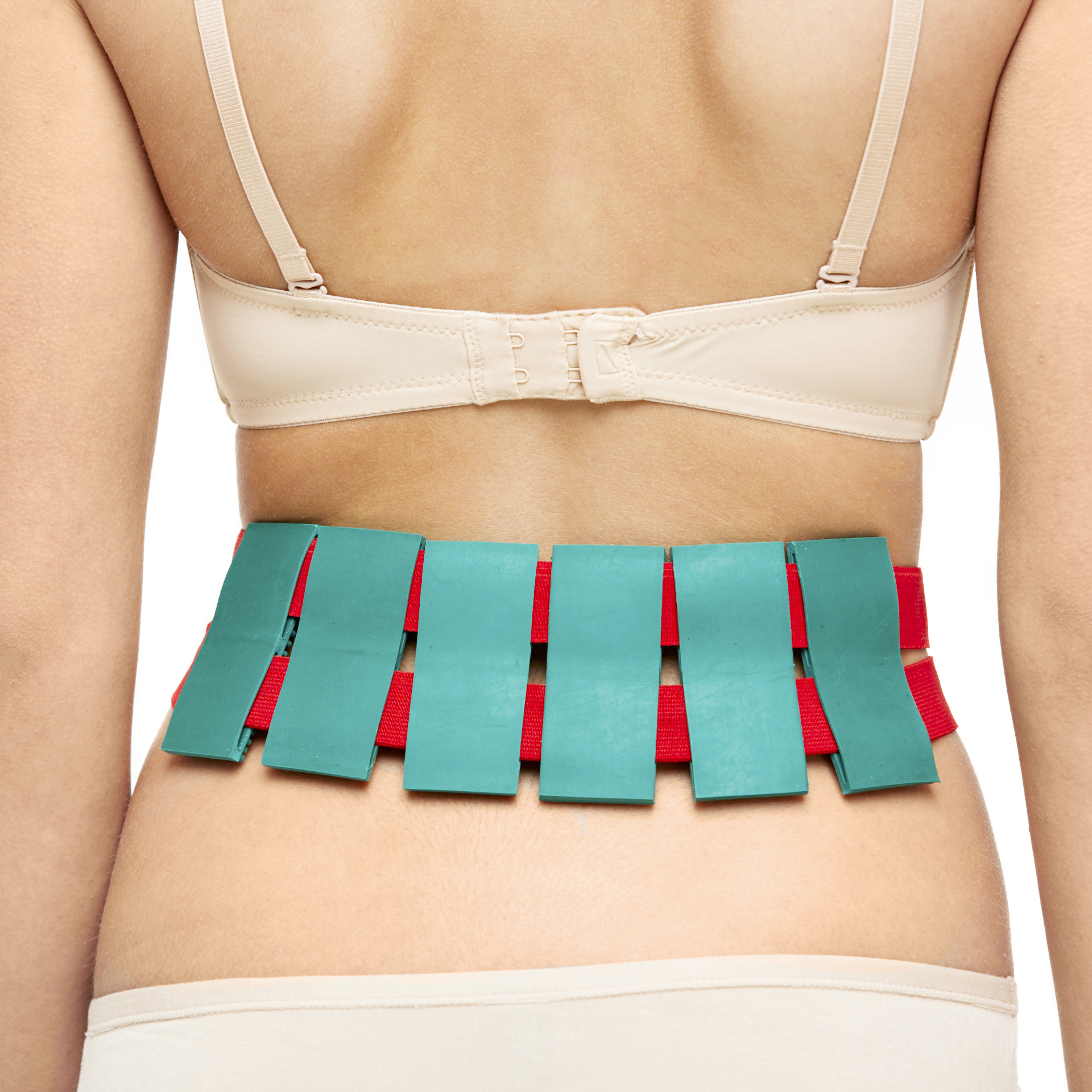 |
Use of ointments with warming is recommended after applications.
Multineedle therapy by Lyapko applicators is well combined practically with all types of physiotherapeutic treatment.
The good medical effect is reached only in case of correct implementation of references and individual selection of zones and methods of influence.